Unique effect with aXivite
Weight loss, gut health and zonulin levels
Quorum sensing inhibitor
To further research the effect aXivite has on gut health and weight loss, a study was done on phenylcapsaicin as a quorum sensing and swarming inhibitor for gastrointestinal (GI) pathogenic bacteria.
The result shows a new effect that reduces the pathogenicity of bacteria unlike capsaicin which do not have this effect. This in turn leads to an improvement in GI inflammatory conditions, such as leaky gut syndrome and improvement in overall GI health. And with phenylcapsaicin influencing the gut microbiome by reducing inflammation and preventing dysbiosis, weight loss is achieved.

What is Quorum sensing?
Bacteria become pathogenic and significantly increase in numbers in a host by quorum sensing (QS). Quorum sensing is a cell-to-cell communication mechanism leading to differential gene expression in response to high population density. Via this process a particular species of bacteria forms biofilms and the individual cells begin to act as one larger tertiary organism, a team. This communication between the bacteria is done via chemical messages called autoinducers, signalling molecules that are produced in response to changes in cell-population density. QS is responsible for several establishment of bacterial infections virulence genes in the body so to reduce the population of these bacteria and inactivating the QS system of a bacterial pathogen can result in a significant decrease in virulence factor production.

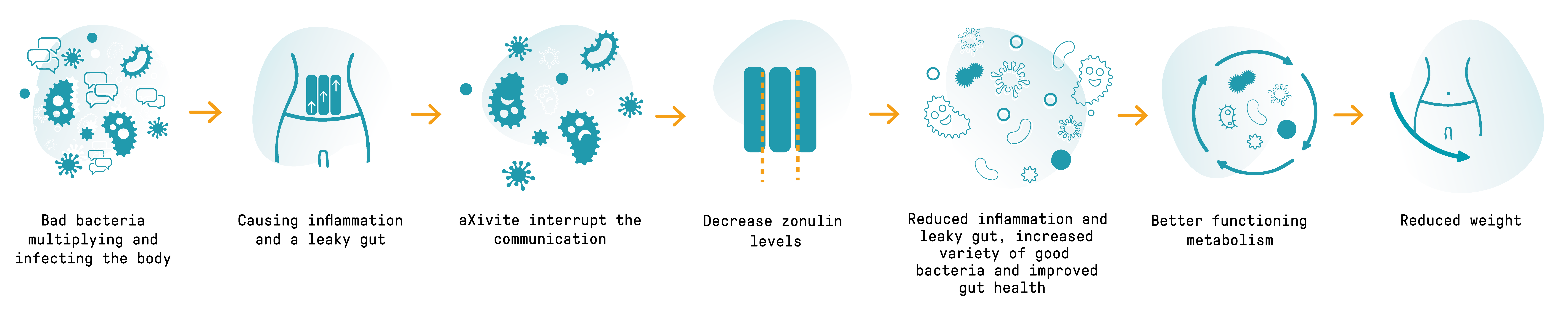
About the study
The study focused on interfering with the QS system using small molecules to block the activation of the AHL receptor protein normally used as the autoinducers. To identify QS-inhibition Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 was used.
Result
In this CV026 bacteria QS inhibition analysis, Phenylcapsaicin was shown to be a QS inhibitor in a dose-dependent manner with a strong to weak QS inhibiting activity in a responsive way, while showing antibacterial activity at higher doses. The result shows that phenylcapsaicin may have a new, unanticipated effect that reduces the pathogenicity of bacteria. This in turn leads to an improvement in GI inflammatory conditions, such as leaky gut syndrome and improvement in overall GI health. With phenylcapsaicin influencing the gut microbiome, it is then likely to contribute to weight loss by reducing inflammation and preventing dysbiosis. Serum levels of the critical gut barrier marker, zonulin, showed a statistically significant decrease for the low dose treatment group over the 8 week period. Human zonulin is a protein that increases permeability in the epithelial layer of the small intestine by reversibly modulating the intercellular tight junctions. Treatment that lowers this circulatory marker can be considered a method to promote improved gut health.
